LLM-based Agent and Multi-agent System
Wenyue Hua
Nov 28, 2023
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence (AI) aims to emulate Human Intelligence (HI) in combining basic skills to address complex tasks. AI agents is an especially important step the development of AI, which should integrate expert models and external tools for solving intricate problems, a step towards achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate notable capabilities in learning and reasoning and are proficient in employing external models, tools, plugins, or APIs for complex problem-solving. LLM-based agents are essentially LLMs enhanced with access to these additional resources.
Wenyue Hua
Postdoctoral Researcher
Ph.D. in artificial intelligence, specifically focused on large language models.
Publications
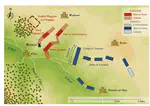
Can we avoid wars at the crossroads of history? This question has been pursued by individuals, scholars, policymakers, and organizations throughout human history. In this research, we attempt to answer the question based on the recent advances of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs). We propose WarAgent, an LLM-powered multi-agent AI system, to simulate the participating countries, their decisions, and the consequences, in historical international conflicts, including the World War I (WWI), the World War II (WWII), and the Warring States Period (WSP) in Ancient China. By evaluating the simulation effectiveness, we examine the advancements and limitations of cutting-edge AI systems’ abilities in studying complex collective human behaviors such as international conflicts under diverse settings. In these simulations, the emergent interactions among agents also offer a novel perspective for examining the triggers and conditions that lead to war. Our findings offer data-driven and AI-augmented insights that can redefine how we approach conflict resolution and peacekeeping strategies. The implications stretch beyond historical analysis, offering a blueprint for using AI to understand human history and possibly prevent future international conflicts. Code and data are available at this url.
Wenyue Hua,
Lizhou Fan,
Lingyao Li,
Kai Mei,
Jianchao Ji,
Yingqiang Ge,
Libby Hemphill,
Yongfeng Zhang
Human Intelligence (HI) excels at combining basic skills to solve complex tasks. This capability is vital for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and should be embedded in comprehensive AI Agents, enabling them to harness expert models for complex task-solving towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). Large Language Models (LLMs) show promising learning and reasoning abilities, and can effectively use external models, tools, plugins, or APIs to tackle complex problems. In this work, we introduce OpenAGI, an open-source AGI research and development platform designed for solving multi-step, real-world tasks. Specifically, OpenAGI uses a dual strategy, integrating standard benchmark tasks for benchmarking and evaluation, and open-ended tasks including more expandable models, tools, plugins, or APIs for creative problem-solving. Tasks are presented as natural language queries to the LLM, which then selects and executes appropriate models. We also propose a Reinforcement Learning from Task Feedback (RLTF) mechanism that uses task results to improve the LLM’s task-solving ability, which creates a self-improving AI feedback loop. While we acknowledge that AGI is a broad and multifaceted research challenge with no singularly defined solution path, the integration of LLMs with domain-specific expert models, inspired by mirroring the blend of general and specialized intelligence in humans, offers a promising approach towards AGI. We are open-sourcing the OpenAGI project’s code, dataset, benchmarks, evaluation methods, and the UI demo to foster community involvement in AGI advancement here this url.
Yingqiang Ge,
Wenyue Hua,
Kai Mei,
Jianchao Ji,
Juntao Tan,
Shuyuan Xu,
Zelong Li,
Yongfeng Zhang